The proteins in plant-based meat alternatives may not be as accessible to human cells as those in real meats. meata new study has suggested.
Weather floors rich in proteinWhat soy beansare commonly used around the world, researchers, including those at The Ohio State University in the US, say it’s unclear how much of the nutrient reaches human cells.
In the study published Wednesday in the Journal of Food and Agricultural Chemistry, The scientists tested whether human cells grown in a lab take up the same amounts of the protein building block peptides from meat alternatives as they do from chicken.
The findings may lead to new ingredients that can increase the absorption of nutrients from plant-based meat products, the researchers say.
To mimic the look and texture of real meat, they say plant-based substitutes are usually made by dehydrating powdered plants and mixing them with seasonings.
These mixes are then typically heated, moistened and processed through an extruder to produce plant-based meat, the researchers say, adding that these products are often thought to be more nutritious since the plants used to make them are rich in protein and low in undesirables. fats
However, the researchers say the proteins in the substitutes may not be broken down into peptides as well as those in meats.
In the new study, they looked at the amount of peptides taken up from a model meat alternative by human cells and compared it to the amount the cells took up from a piece of chicken breast (CB).
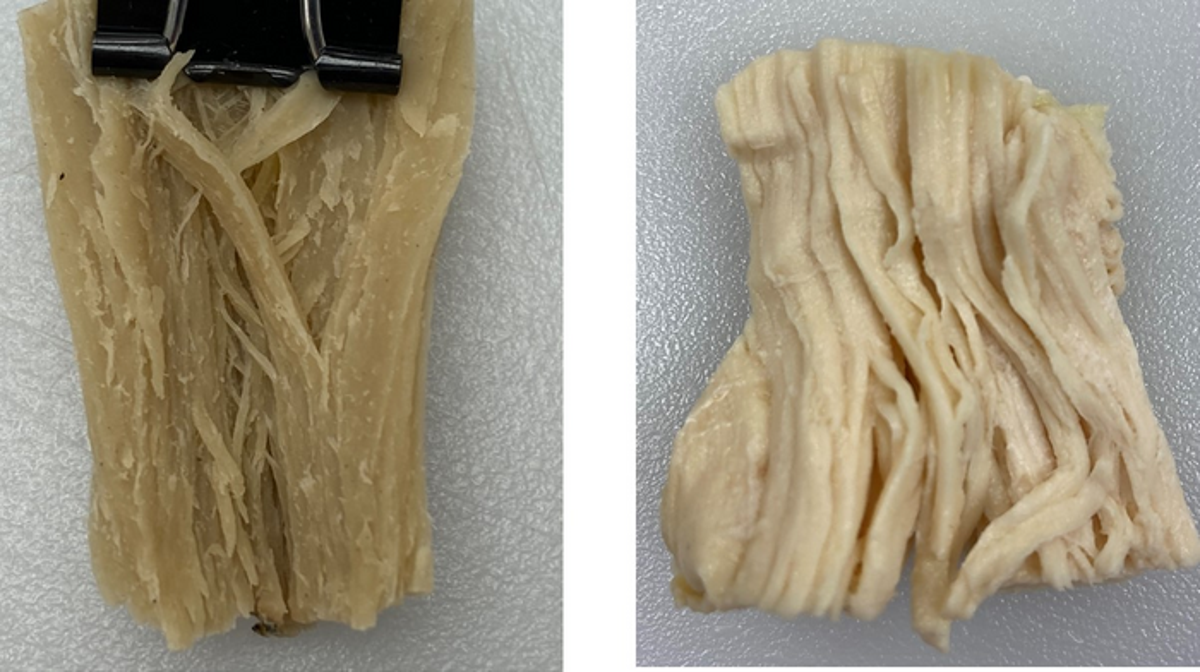
For the research, the scientists created a model meat alternative (MA) made from soybeans and wheat gluten with the extrusion process.
When it was opened, they say the material had long stringy pieces inside, like chicken.
The researchers then cooked pieces of the substitute and chicken meat, breaking them down using an enzyme that humans use to digest food.
They found that the peptides and their amino acid building blocks from meat substitutes were less soluble in water than those from chicken, and were also not “absorbed as well by human cells.”
“The amino acid composition showed fewer essential and non-essential amino acids in the MA permeate than in the CB permeate,” the scientists wrote in the study.
They say future studies may help identify ingredients that may help increase the absorption of peptides from plant-based meat substitutes.