From improving cardiovascular health to boosting immunity, the reported benefits of omega-3s have made fish oil one of the most sought-after dietary supplements. But can there really be any tangible health benefits from increasing your daily omega-3 intake?
Omega-3 is a general term used to describe a group of unsaturated fatty acids with a specific double bond in their chemical structure, such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). ).
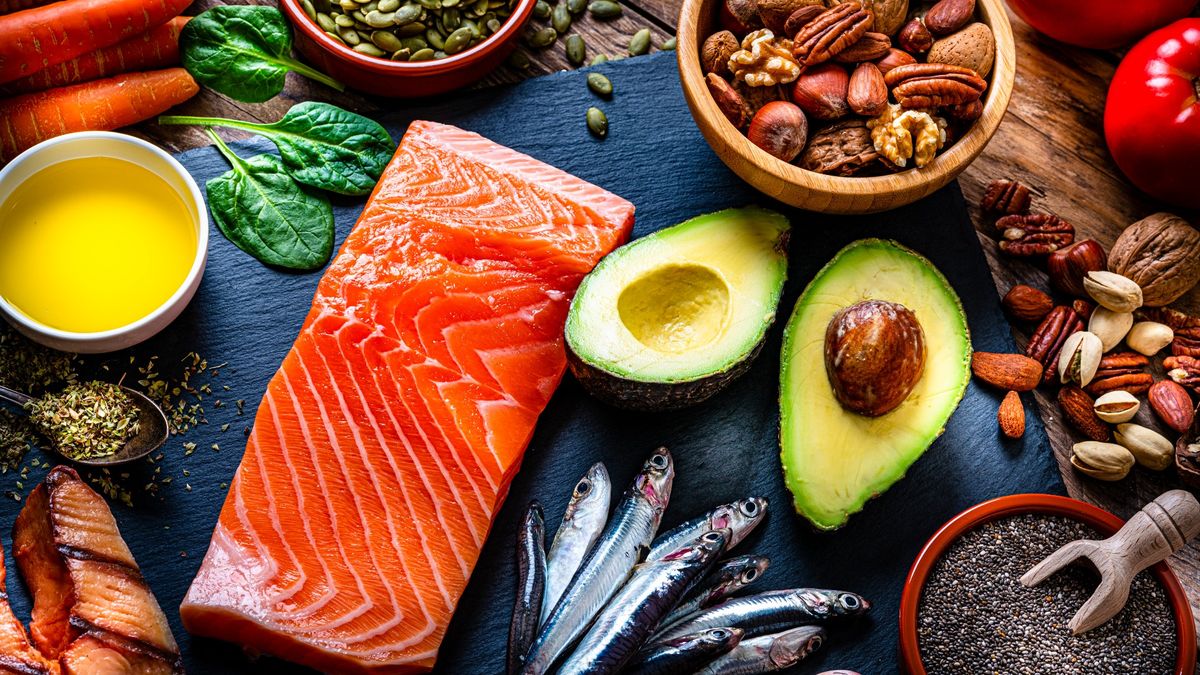
“They’re known as ‘essential fatty acids’ because our bodies can’t create them and we can only get them through our diet,” says Dr. Claire Thomas, physician and clinical content leader at perennial life (opens in a new tab). “In addition to dietary supplements, there are some excellent sources of omega-3s found in other foods. Unsurprisingly, fatty fish like mackerel, salmon, and herring are packed with omega-3s. Walnuts, soybeans, and chia and flax seeds are also great meatless options.”
Scientists have been studying the potential benefits of omega-3s for years. According to the nutrients (opens in a new tab) magazine, these nutrients have been shown to be the key factor in reducing inflammation levels, an important risk factor for multiple chronic diseases. In fact, omega-3 may be crucial for our cardiovascular, nervous, and immune systems.
“Some studies indicate that its anti-inflammatory properties may also have benefits for conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory and degenerative conditions of the joints and inflammatory bowel diseases,” says Thomas.
Here, we take a deep dive into the science of essential fatty acids to give you a better understanding of how these nutrients can affect our minds and bodies.
1. Supports cardiovascular health
One of the most widely researched benefits of omega-3s applies to our cardiovascular system, with most studies suggesting that it has a highly protective effect on our hearts. According to an important Cochrane systematic review (opens in a new tab)these fatty acids can significantly reduce the risk of dying from coronary heart disease and cardiac events, while ALA may also help prevent arrhythmia.
Omega-3 can improve our cardiovascular health in several ways. “They are essential for producing hormones that regulate blood coagulation, the contraction and relaxation of artery walls, and inflammation,” says Abbas Kanani, a pharmacist at chemical click (opens in a new tab). “This may be beneficial for cardiovascular disease as they work to reduce plaque in the arteries of the heart.
Omega-3 fatty acids can also improve the function of the endothelium, a thin membrane that lines the inside of the heart and blood vessels. As described in atherosclerosis (opens in a new tab) daily, that’s because they can help control how much fluid is carried in the blood and how the blood vessels dilate and constrict.
Studies (opens in a new tab) Studies in overweight patients with metabolic syndrome have also shown that omega-3s can help balance blood lipids, particularly by lowering levels of ‘bad’ LDL cholesterol.
However, it should be noted that a significant number of studies over the years have shown no significant link between omega-3s and heart health. The scientists suggest that these differences may be related to the doses used in the tests.
2. Can Boost Immunity
Recently, scientists have discovered another potential benefit of omega-3s: a healthier immune system. Studies (opens in a new tab) have shown that these fatty acids can affect the composition of our gut microbes, which in turn can have a positive impact on our gut health. Since our digestive system is the first line of defense against harmful microbes, omega-3s can have an indirect, but powerful, effect on our entire immune system.
These fatty acids have also been shown to stimulate antibody production and regulate white blood cell function, as described in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences (opens in a new tab).
3. Keeps your brain healthy
Omega-3s may be essential for the proper functioning of our central nervous system and, in particular, the brain. In fact, they have been shown to prevent or slow the progression of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, as reported in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences (opens in a new tab).
There are several reasons why these fatty acids can benefit our nervous system. According to an article in Frontiers in the neuroscience of aging (opens in a new tab), these compounds are found in abundance in brain cell membranes and can affect how neurons communicate with each other. And according to another review in the nutrients (opens in a new tab) journal, DHA is one of the key components of healthy brain and eye development. This particular fatty acid may also play an important role in mental health during early childhood. Evidence suggests that low omega-3 intake may increase the risk of developing attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, bipolar disorder, and depression.
“Studies indicate that those who consume omega-3s regularly are less likely to experience depression,” adds Thomas. “Although the studies suggesting that EPA helps with more serious neuropsychiatric disorders are relatively recent, they seem to indicate that there is a link.”
4. Contributes to eye health
Since omega-3 is an important structural component of the retina, it plays an important role in eye health. The role of the retina is to capture the light that enters your eye and translate it into the images you see. Without these crucial fatty acids, you may experience problems with your eyesight.
“Omega-3 optimizes the variability of photoreceptor membranes, retinal thickness, function, and provides a protective role,” says Kanani. “Healthy levels of DHA also protect against damage caused by exposure to bright light and oxidative stress.”
scientists from The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (opens in a new tab) suggest that these fatty acids may even protect against neovascular eye diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration. Both conditions can lead to blindness, and both lack treatment options that are free of adverse side effects.
5. It can improve the health of your skin
One of the lesser-known benefits of omega-3s, and EPA in particular, is that it can contribute to healthier skin.
“A healthy intake of EPA can help not only keep skin hydrated, but also reduce the risk and effects of acne,” says Thomas. In fact, as described in a study by the Dermatology Clinics (opens in a new tab) journal, omega-3 can help improve skin hydration and balance its oil production, as well as reduce the risk of premature aging. In fact, these fatty acids may be the key to effective treatment of inflammatory skin conditions.
As reported in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences (opens in a new tab)combined omega-3 and omega-6 supplementation appears to be effective in treating symptoms of atopic dermatitispsoriasis and acne.

6. Keeps your bones healthy
Some of the benefits of omega-3 may be related to bone health. A review on the British Journal of Nutrition (opens in a new tab) reported that a significant number of studies suggest that these fatty acids may help improve bone mineral density and various markers of bone turnover. According to a meta-analysis published in the Climacteric (opens in a new tab) magazine, omega-3 may particularly affect osteocalcin levels in postmenopausal women. Osteocalcin is a protein hormone involved in the maintenance and regeneration of bone tissue, and postmenopausal women are at particularly high risk of developing osteoporosis.
However, it is worth mentioning that a significant number of studies produced quite conflicting results. Nevertheless, scientists (opens in a new tab) have recently discovered that different sources of omega-3 may have a different effect on bone remodeling processes. For example, flaxseed oil may be better for improving bone structure, while fish oil may promote higher bone mineral density.
“The anti-inflammatory properties found in omega-3s can help reduce the intensity of pain in many of the joints in your body, with studies showing that it can significantly improve joint pain in people with Rheumatoid arthritisKanani adds. “They also form the backbone of prostaglandins, which regulate our immune system and fight joint inflammation.”
7. It can affect sleep
A growing body of evidence suggests that omega-3s may play a role in sleep regulation. According to an article in the American journal of clinical nutrition (opens in a new tab)people with higher regular intakes of these fatty acids seem to need less sleep.
In addition, omega-3 fatty acids can help improve sleep in babies. This may be because they help organize and mature your sleep-wake routine, without having an effect on the duration or overall efficiency of sleep.
