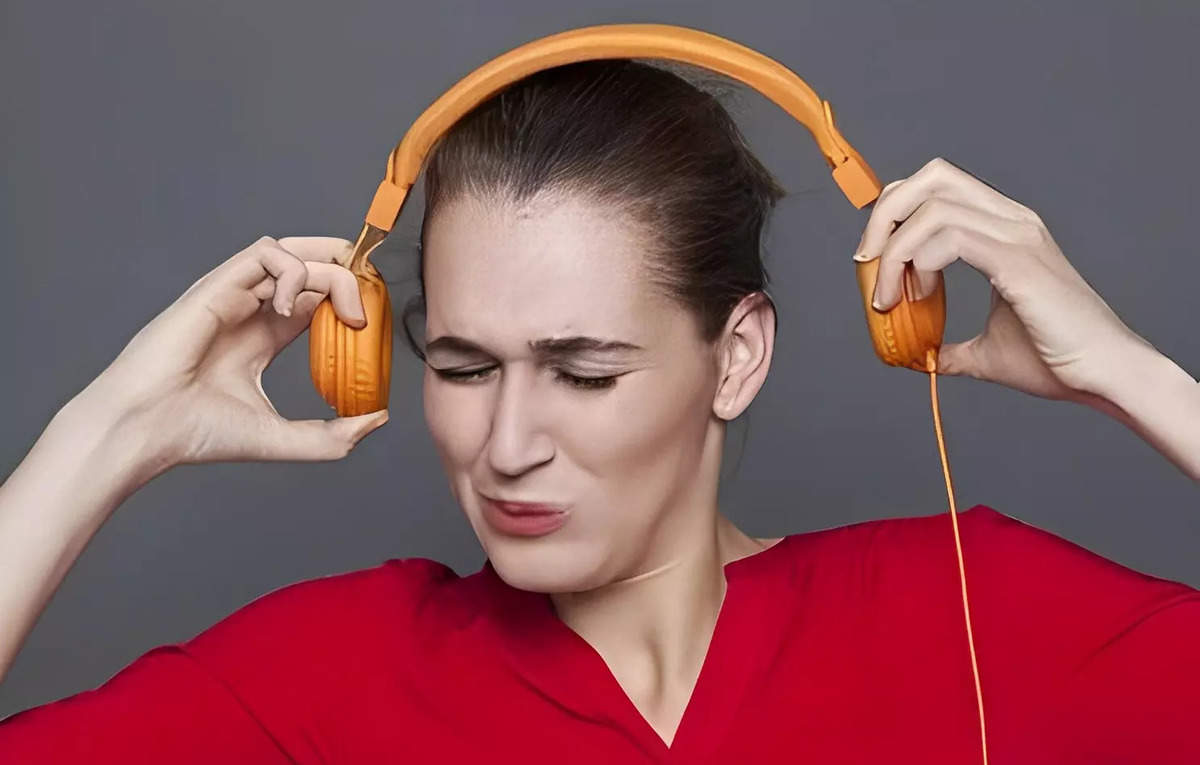
New Delhi: Constant ringing in the ears, whether it be from listening to loud music or having endless conversations and attending constant office meetings, is pushing many young people to sensorineural hearing loss. Nearly 1.1 billion young people are at risk of life-threatening diseases hearing lossdue to the increase noise exposure, inform the experts. They warn that Millennials and GenZ are prone to induced noises hearing loss.
According World Health Organization (WHO), by 2050, it is projected that nearly 2.5 billion people will have some degree of hearing loss and at least 700 million will require auditory rehabilitation. Over a billion young adults are at risk of permanent, preventable hearing loss due to unsafe listening practices. The sound waves of headphones they reach our ears and make the eardrum vibrate. This vibration travels through the tiny bones to the inner ear and into the cochlea, the fluid-filled chamber in the inner ear made up of thousands of tiny “hairs.” When this vibration reaches the cochlea, the fluid vibrates and causes the hair to move. The louder the sound, the stronger the vibration, and the more the hair moves, the more it is damaged.
Speaking to ETHealthworld, otolaryngologists and audiologists report that there has been a dramatic increase in patients with neural loss in the last two years, particularly post-COVID due to the increased use of headphones and headphones.
Constant noise exposure puts hearing at risk
Increased noise exposure can be in any form, but more due to constant use of headphones and headphones connected to smart devices leading to sensorineural hearing lossreported Prarthana Jagtap, MD, ENT Consultant, Global Hospitals, Parel. “The WHO sets hearing limits. These devices can produce sounds up to 120 decibels, which can severely damage cells in the inner ear, and even 10-15 minute exposure, anything over five minutes can cause hearing damage. permanent at those levels,” he added.
Speaking about how hearing aids damage the ear by causing hearing fatigue, Dr G Srinivas Reddy, Senior Consultant, Ear, Nose, and Throat Surgeon, Apollo Hospital, Hyderguda, said: “Occupational noise is the most frequently studied type of noise exposure. A recent addition is ambient noise from regular traffic and exposure to social noise, such as the use of Personal listening devices (PLD) from mobile phones or MP3 players, which have become an inseparable part of our daily life, is causing tinnitus (ringing sensation) and hearing loss. It also leads to non-auditory effects such as cardiovascular diseases and general well-being such as headache, lack of concentration; increased stress and anxiety; learning disabilities, discomfort, sleep disturbances and inability to concentrate.” Clarifying further, Dr. ChandraVeer Singh, Consultant ENT, Head and Neck Surgeon, Wockhardt Hospitals, said: “Basically, our ear is made up of three compartments . The first is the outer layer, the other is the middle layer that contains the cochlea and nerve, and the third is the inner ear. These Bluetooth headsets and devices create sensorineural hearing loss. They damage the inner hair cells that are responsible for hearing. This is more in people 40 to 50 years earlier, but today because of headphones or earplugs, there is a higher incidence of hearing loss in people of much younger age.”
Dr. Singh added that every week, three to four patients complain of pain or noise-induced hearing loss and it is the age group of the younger generation. The inner ear containing outer and inner hair cells is damaged by the devices.
Mentioning the decibels that can lead to hearing loss, Dr. Garima Vegivada, audiologist and clinical director of the Hear ‘N’ Say clinic, stated that exposure to 85 dB, for 8 continuous hours a day, can cause loss hearing loss and as sound levels increase to 90-95 dB, shorter duration also causes hearing loss. A decibel ranging from 105 to 110 dB can cause damage to the ears in five minutes.
Often times, to isolate themselves from the crowded and noisy world, many plug into these devices to fence them off, but they don’t realize that such relaxation for an extended period of time is creating irreparable loss to the ears and even the brain. Otolaryngologists report that smart devices such as AirPodsBluetooth, headphones or headphones have an irreversible impact.
Transition from smart hearing aids to hearing aids
Noting that there has been a dramatic increase in patients with neural loss in the past two years, post-COVID due to increased use of hearing aids and earphones, Dr Jagtap said: “As a device gets smaller, it penetrates deep into the ear and tends to have the propensity to produce greater amounts of damage.If it is more than 100 decibels, even 15 minutes can damage the ears.Many to overcome ambient noise tend to increase the volume of the music they listen to, without realize that they are crossing the dangerous threshold limit.”
Speaking of Bluetooth devices, Dr Singh said: “The lightning coming from the Bluetooth device which is known for electromagnetic field technology poses serious health problems. Many say that these rays can cause cancer, but it is not yet proven. But these rays will definitely cause headaches, migraines and bluetooth devices are more dangerous and headphones are less dangerous, they will produce less suffering from hearing loss compared to airpods.”
Additionally, Dr. Vegivada reported that sharing AirPods can transfer bacteria, which can cause ear infections. Prolonged use will cause ear pain, and since AirPods come in a standard size, not custom-made, wearing the wrong size earbuds pushes this hard plastic into the skin and cartilage of the ear, causing unnecessary pressure and discomfort.
Doctors report that prolonged pressure on the ears will lead to noise-induced hearing loss: tinnitus (tinnitus symptoms are a constant ringing, ringing, or ringing in one or both ears), hyperacusis, hearing loss, or dizziness.
Reduce Noise Clutter: The Only Option
Doctors advise that the rule is 60/60, 60 decibels can be heard for 60 minutes, then the ears should be given rest. According to experts, there can be both temporary and permanent damage.
“In temporary damage, medication can reverse the loss, but a higher percentage of people who have been exposed to these loud noises suffer a permanent threshold shift and that, unfortunately, is irreversible and eventually you have to move on to rehabilitation. with headphones and other things. said Dr. Jagtap.
Dr. Vegivada suggests using any headphones less than two hours a day with a sound level below 70-80 dB, or switching to far speakers or devices like Alexa at a considerable distance to prevent hearing loss.
“Most people who wear hearing aids use it with their smart devices. And a lot of them started to come with built-in controls. Now, you can go into your settings and tweak that without going over the threshold. You can avoid unintentional damage. Take breaks from headphones is a must. For people who have occupational exposure and cannot avoid using these devices, regular hearing screening is mandatory,” added Dr. Jagtap.
Ear, nose, and throat doctors and audiologists say that any personal listening device can create an oasis of privacy, but long, incessant use is harmful. They report that only self-actualization in limiting decibel levels and instilling healthy listening habits will help them prevent long-term hearing loss.