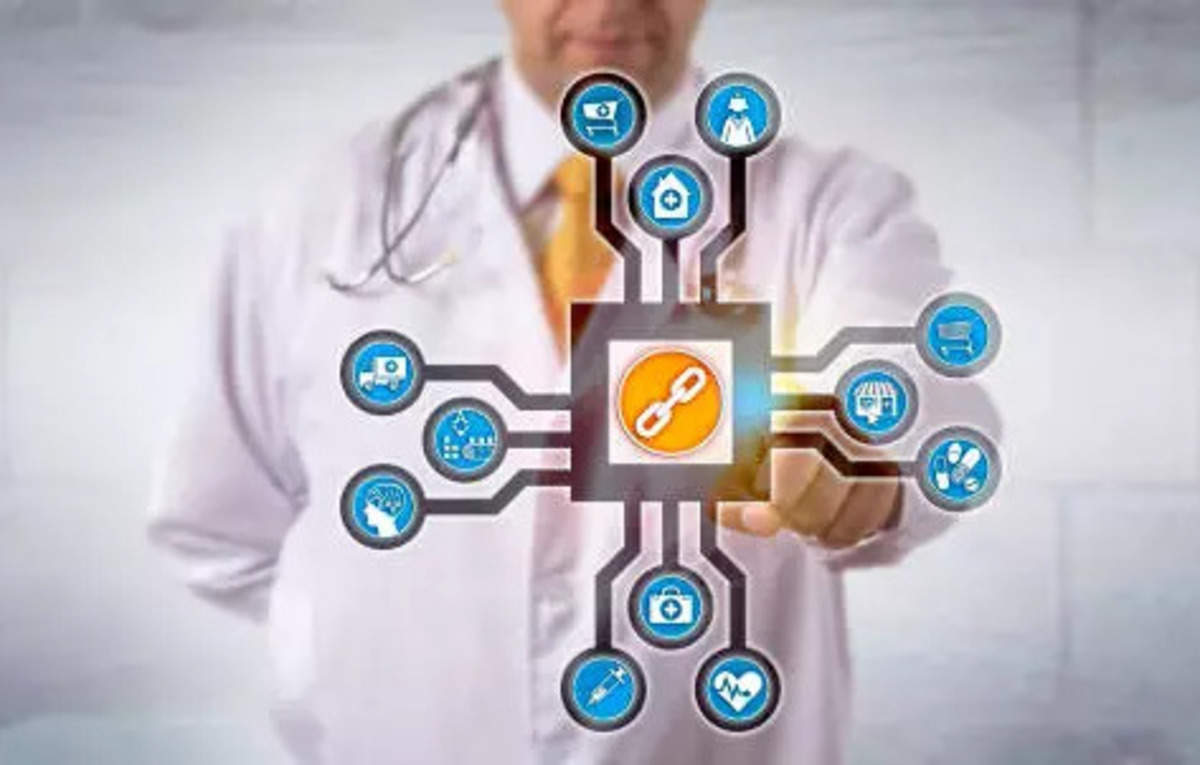
New Delhi: Public health as an issue is of paramount importance to all nations. Especially India, with its 1.4 billion people, faces an uphill task to provide universal and affordable healthcare. Without harnessing technology at scale, such aspirations will remain a pipe dream. It is important to highlight that the COVID-19 pandemic it has shown the world that technology can not only be a great enabler, but also the backbone of the public health service delivery system. India’s successful monitoring of patients and vaccination of citizens, as well as the issuance of digital certificates through the CoWIN app, is a good example. In recent years, emerging technologies such as AI (artificial intelligence), ML (machine learning) and big data have made inroads in the healthcare sector. Increasingly, block chain-which is more discussed in the financial sector- has also made its presence in the health sector. Importantly, the characteristics of blockchain technology make it suitable for wide use in healthcare projects that run at scale.
Distinctive features of blockchain:
Blockchain as a technology is endowed with those characteristics that make it suitable for use in the health sector in multiple ways. From drug research and discovery to patient medical record keeping, blockchain can improve efficiencies across the industry. First of all, blockchain is a form of decentralized ledger technology that allows for the secure storage and transmission of data. Here, every transaction is recorded on every node in the network. Therefore, no record can be changed without altering any subsequent blocks in the chain. This makes the entire system tamper-proof. Secondly, such decentralization of data registration provides security and stability to the stored information. Privacy and data security are guaranteed thanks to these features. This is critical, as data ownership and management remain in the hands of a few. Since healthcare supply chains are complex, blockchain-based solutions provide much-needed financial and logistical traceability.Benefits of blockchain in healthcare:
The benefits of blockchain in healthcare are many. Blockchain-based solutions are now being leveraged in the pharmaceutical industry, healthcare delivery through public and private institutions, public policy making, and pandemic-like control, among others. Its uses in India are immense as the country takes various initiatives to improve its healthcare system.
Telehealth:
A country like India is facing a severe shortage of healthcare officials including doctors. Each allopathic doctor in India provides medical care to at least 1,511 people, far more than the World Health Organization norm of one doctor per 1,000 people. The shortage of trained nurses is even worse with a nurse to population ratio of 1:670 versus the WHO norm of 1:300. To ensure access to quality healthcare, the Indian government has been running a telemedicine programme.eSanjeevani‘ in addition to throwing Tele-MANAS in the space of mental well-being. Not only government institutions but also a large number of private healthcare providers have been providing telehealth facilities to patients as well. Blockchain-powered solutions can be a game-changer in the telehealth space, as they will record all patient-related information that can be accessed by multiple doctors at every stage of treatment. In the same way, it will help doctors and other health officials to access the patient’s history every time they go for a consultation. Therefore, better healthcare delivery at scale is possible by leveraging blockchain technology.
Additionally, blockchain solutions can verify the credentials of healthcare professionals in India. The country has seen multiple cases of fake doctors and quacks treating patients, leading to fatal consequences. An earlier report by the World Health Organization (WHO) had noted that 57 percent of Indian doctors were quacks and most came from rural regions. In this context, healthcare delivery in rural areas can be greatly improved by leveraging blockchain technology.
Efficient immunization program:
Universal Immunization Program is one of the largest such initiatives in the world, taking place in India. Such programs have massive amounts of logs generated and stored. For example, the successful immunization program against polio National Health Mission It generates a large amount of data, which is extensively monitored, analyzed and reported to demonstrate its coverage. Similarly, other immunization programs such as vaccination against Yellow Fever are tracked through the issuance of vaccination cards. However, such monitoring and analysis is done by keeping paper records. This leads to the possibility of losing data. This practice is also considered a factor in why the universal immunization program does not cover all intended beneficiaries. Therefore, a digital health record is the need of the hour. In this regard, government and private agencies can take advantage of blockchain-powered solutions to create digital health records of all eligible beneficiaries. Such digital health records can also be created for each citizen of the country to create a repository.
Encouragingly, the Indian government is in the process of creating digital health records through its initiatives, including ‘Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission’ (ABDM) and ‘Ayushman Bharat Health Account‘ (ABHA) numbers. Hopefully, blockchain-powered solutions will be leveraged to make these initiatives successful.
Formulation of complementary policies:
In a country like India with a large population, a specific approach is required for the incidence of various diseases. This can be achieved if the correct policy and subsequent interventions are carried out in a timely manner. However, the delivery of a good public health service depends on the timely availability of good data together with the ability to authenticate the sources of the data. Since health surveillance and monitoring requires cross-sector data correlation, the inclusion of blockchain technology to anchor records can lead to better outcomes for both the state and its citizens.
In addition to these benefits, the blockchain-backed implementation for health records ensures data privacy and security, as data is subject to greater control with restricted access. This technology can also be used to reduce healthcare costs by automating many data recording and related tasks. For a country like India, blockchain-based solutions are the best tools to ensure healthcare delivery at scale. Encouragingly, many global and national organizations have already begun implementing blockchain-based solutions in the healthcare sector. As adoption increases, global blockchain technology in the healthcare market is projected to reach $16.30 billion by 2031 from $532 million in 2021.
Although blockchain use cases are increasing in the healthcare sector, risks remain. The privacy and confidentiality of patient data remains sacrosanct and must be protected at all costs. Therefore, access and control of blockchain-based systems must be restricted in addition to proper implementation. From this perspective, institutions and companies must collaborate with the right technology partner to harness the true potential of blockchain in the healthcare sector.
Sankarshan Mukhopadhyay, Vice President of Customer Experience at Dhiway
(DISCLAIMER: The views expressed are solely those of the author and are not necessarily endorsed by ETHealthworld. ETHealthworld.com shall not be liable for any damage caused to any person or organization directly or indirectly.)