In the late 1970s, smallpox was eradicated worldwide thanks to large-scale vaccination programs. Smallpox is a highly contagious and deadly disease caused by the variola virus. The monkeypox virus (MPXV) currently circulating is closely related to the smallpox virus. Previously, MPXV was endemic only in sub-Saharan Africa, but has since spread throughout the world. Older people who have received the smallpox vaccine should be adequately protected against poxviruses. A recent review by Barbara S. Schnierle of the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, Germany, and published in the journal virus summarized what is known about MPXV, the disease it causes, and strategies to slow its spread.
Check: Monkeypox Goes North: Ongoing Monkeypox Infections Worldwide in Humans. Image Credit: Cristian Storto / Shutterstock
Background
MPXV became the most common zoonotic orthopoxvirus infection in humans after the eradication of the smallpox virus (VARV). It was first identified in 1958 in Denmark among macaque monkeys, and later, in 1970, human cases were reported in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Infections occurring primarily in children have been reported sporadically in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and other countries in central and western Africa. Unlike variola virus, which persisted only in primates, MPXV can infect many species.
Rodents, African squirrels, and nonhuman primates have been described as reservoirs for MPXV. There are two distinct genetic clades of MPXV, namely clade I (Central African or Congo Basin (CB) clade) and clade II (West African (WA) clade). Mortality rates for Clade I and Clade II have been reported to be 10.6% and 3.6%, respectively, and a 10 kbp deletion in Clade II has also been observed by genomic analysis.
The current outbreak is driven by Clade II, and the World Health Organization (WHO) had confirmed 25,047 cases, for 2North Dakota August 2022, out of Africa. 99% of the cases were men with a median age of 36 years and 98% were men who have sex with men (MSM). The global spread of MPXV was declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) by the WHO in July 2022.
Clinical disease caused by MPXV
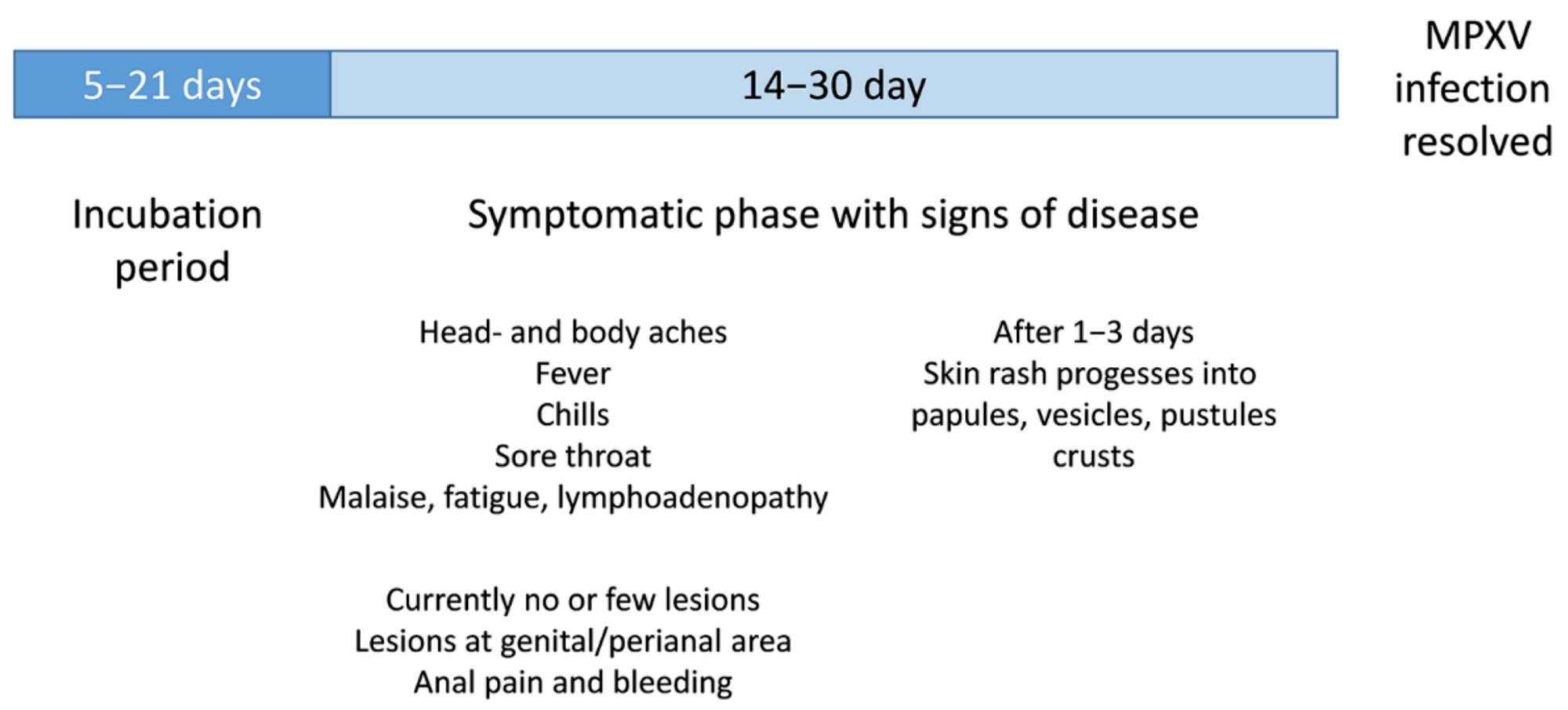
The incubation period for MPXV is usually 5 to 13 days, but can be as long as 21 days. The first symptoms include severe headache, fever, sore throat, nasal congestion, cough, etc. Within the first three days of the onset of fever, a rash may appear on the face and extremities. A loss of vision is also possible as the cornea is affected.
The initial rash eventually dries up and falls off after going through the stages of papules, vesicles, pustules, and crusts. The number of injuries varies between individuals and can range from a few to several thousand. In the current outbreak, lesions appear mainly near the genitals or anus, but other places, such as the feet, face, and chest, are not uncommon. Severe cases can occur in pregnant women, children, and immunosuppressed people.
Diagnosis and treatment
The symptoms are quite similar to those seen in cases of measles or chickenpox. The material from the skin lesion comprises an adequate amount of MPXV for the PCR test. In addition, detection of MPXV-specific IgM could indicate infection; however, serological tests could be negatively affected by recent vaccination.
To prevent orthopoxvirus infections, vaccination is considered the most effective. Smallpox vaccines are expected to be 85% effective against MPXV. The smallpox vaccine ACAM2000, licensed in North America, is given as a single dose with a bifurcated needle. However, it cannot be used in immunosuppressed people.
LC16m8 is a third generation vaccine licensed in Japan. It is derived from the Lister strain of vaccinia virus (VACV) and has shown an improved safety profile. It has the same exclusion criteria as ACAM2000 but has been shown to be effective in animal models. In addition, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have approved a fourth-generation vaccine based on modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA) for adults only.
In addition, immunization with vaccinia immunoglobulin (VIG) isolated from blood samples of individuals vaccinated with smallpox vaccine can be administered intravenously. Brincidofovir and Tecovirimat (ST-246) are two oral drugs that were approved to treat smallpox but have been shown to be effective against MPXV in animals. The former is approved in the US, while the latter has been approved for emergency use by the FDA and the EMA.
future perspective
The cessation of smallpox vaccination in 1980 has been considered to be the main driver of the current MPXV outbreak, as it made younger people vulnerable to infection. In this era of global travel, disease surveillance in endemic and non-endemic regions is essential. It is unclear whether MPXV 2022 differs in transmissibility, host switching, or pathology from previous isolates. Future research urgently needs to investigate this topic.
Smallpox vaccines are likely to be effective against MPXV. Since the current outbreak is concentrated in the MSM community, vaccination should be offered to MSM, close contacts, and health care workers. Furthermore, large-scale vaccination campaigns could be organized in endemic regions to eliminate possible future outbreaks.
.