Mandi: Researchers at the Mandi Indian Institute of Technology have analyzed the different factors affecting herding in the adoption of portable technologies for personal health care. They have used mathematical models to analyze data collected from surveys to provide insight into the marketing effectiveness of online reviews. The results of the research have been published in the Journal of Marketing Communications. The research has been led by Dr. Saumya Dixit, assistant professor in the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, IIT Mandiand co-authored with his PhD student, Ms. Anjali Pathania of IIT Mandi and Dr. Gowhar Rasool, School of Business Studies, Central Jammu University, Jammu.
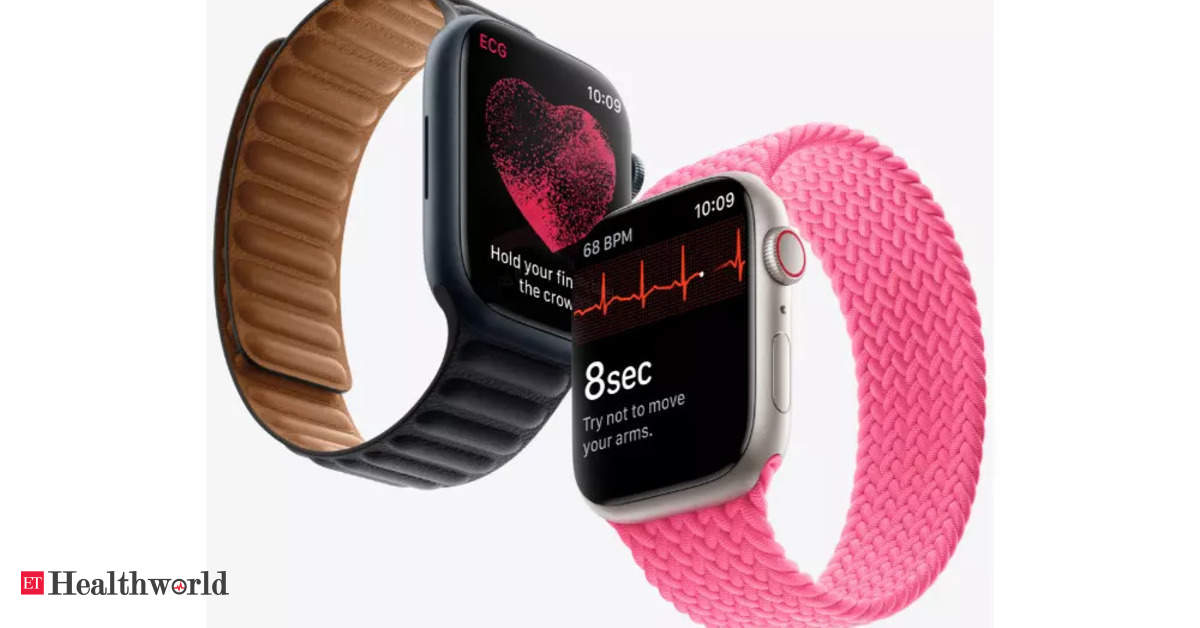
The team’s recent study aims to understand herding drivers in the adoption of wearable technologies for personal healthcare. There has been an increase in the use of such devices since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. Some examples of such devices include fitness trackers, smartwatches, wearable sensors, and wearable medical devices, including the oximeter that was widely used during the pandemic to monitor blood oxygen levels. Wearable devices can connect to a smartphone or other sources to display health-related data and can offer features such as alerts, reminders, and personalized recommendations.
Traditionally, recommendations and reviews from other users have been the main drivers of adoption for any product, including wearable devices. While in the past these reviews were mostly by word of mouth, with the advances of Web 2.0 technologies, consumers can easily and freely share their experiences with services and products on a large scale and in real time through various media, such as social networks, social and online review websites. In modern times, online reviews are the electronic version of Word-of-Mouth, or eWOM, which can influence the behavior of a “herd” or group of people in adopting wearable technology for personal health care.
IIT Mandi researchers sought to understand the role of online reviews in inducing other people to purchase and use wearable technology for personal healthcare. They surveyed 434 wearable technology users and analyzed the data using the Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) method with Smart PLS.
Explaining the technicalities of the research, Dr Saumya Dixit, IIT Mandi, said: “We have proposed an integrated model based on herd behaviour, homophily (peer influence) theory and the principles of extracted uncertainties. of initial trust theory to understand the effects of online communication”. Reviews on the adoption of wearable technology in health care.
The analysis showed that reading reviews written by users with similar backgrounds and needs, combined with usage information related to ease of use, usefulness of wearable technology for personal health care, and company reputation can affect whether potential users decide to adopt or not. of the portable medical device.
Speaking about the other recommendations based on the results of her analysis, Ms. Anjali Pathania, Ph.D. IIT academic Mandi said: “Online review community managers should encourage consumers to provide homophile details while writing reviews along with semi-guided information related to user-friendliness, usefulness and reputation of the technology company. laptop. In addition, filters based on homophile information along with review management systems/algorithms should be provided on online platforms to reduce information overload and improve the adoption of portable personal healthcare devices by potential users. “.